ADHD Breakthrough: Bionic Reading Unlocks New Levels of Focus
Have you ever found yourself reading a page only to realize you haven't absorbed a single word? For many individuals with ADHD, this is a familiar and frustrating experience. But what if there was a way to transform the way we read, making it more accessible and focused for those who struggle with attention? Enter the innovative concept of 'bionic reading'.
Bionic reading is more than just a reading technique; it's a bridge to a world where texts become more than just words on a page. In this blog, we'll explore how bionic reading is not just changing the way we read, but also how it is unlocking new levels of focus and understanding for individuals with ADHD.

What is Bionic Reading?
Bionic Reading is a new way to read that helps you increase your reading speed and understand better. [1]It was made by Renato Casuut from Switzerland.[2] The goal is to make reading easier by guiding your eyes to focus on certain parts of words.[3]
Here's how it works: In Bionic Reading, the few letters at the beginning of each word are bolded. When you see these bold letters, your eyes pay attention to them, and your brain quickly figures out the rest of the word. This method means you don't have to look at every letter, so you can read quicker and still understand everything.[4]
You can use Bionic Reading on different devices, including Google Android and through Google Chrome extensions. You can take any text or word file,[5] change it to Bionic Reading style, and read it using special apps. People with ADHD or dyslexia have found Bionic Reading helpful. It makes reading and understanding easier for them, as their brain fills in the rest of the words, maintaining a consistent reading position. Plus, the dark mode option enhances the reading experience, reducing strain on the eyes.[6]

How Bionic Reading Works To Enhance Focus
Bionic Reading is a special technology that makes reading easier and faster, and it's a game changer in the world of reading apps. Let's break down how it works using simple terms:
- Guiding the Eyes: Bionic Reading adds artificial fixation points in the text that catch your eyes. These points help your eyes move smoothly through the text. This means you can read at a decent pace, stay focused, and not lose focus.[7]
- Highlighting Key Parts: When you use the Bionic Reading app, available on the Apple App Store and Google Play Store, it changes the text to make important parts stand out with just a few letters. This helps your brain complete the word and remember the words better.[8]
- Mix of Techniques: The technology mixes different methods, like fixation and saccade (eye movements), and changes how the text looks. This creates a visual effect that guides your eyes to the important parts, especially useful when reading fiction.[9]
- Faster Reading, Better Understanding: By guiding your eyes in this way, Bionic Reading lets you read quicker by 41 words per minute (or 14%). [10]You don't spend as much time on each word, but you still understand the text well, enhancing reading comprehension.
- Customizable Reading Experience: Bionic Reading can be adjusted to suit your reading style. This makes it easier for you to read in a way that's best for you. The app is also available as a Microsoft Windows application, and its functional software allows you to bookmark your favorite pages and save your last reading position.[11]
You can use it as an extension in Chrome, as a web app on any device, and as an app for Android and iOS. This means you can use it almost anywhere to improve your reading.

The Connection between ADHD and Reading Challenges
The Common Reading Difficulties Of ADHD Individuals
Reading can be a significant challenge for both children and adults with ADHD, and here are the key reasons:
- Sustaining Attention: Reading demands continuous attention, something that individuals with ADHD often struggle with. This makes it difficult for them to stay focused while reading, affecting both kids and adults.
- Difficulty in Decoding Words: Decoding involves identifying and understanding written words. Both children and adults with ADHD commonly face challenges in this area, making reading a strenuous task.
- Working Memory and Planning Skills: Effective reading requires the ability to remember what has been read and anticipate what's next. Individuals with ADHD, whether they are children or adults, might find it hard to use these skills for decoding unfamiliar words, recalling previous text, and understanding the storyline.
- Comprehension Challenges: Grasping the main ideas from a reading passage can be particularly tough for people with ADHD. For adults, this might impact their ability to process lengthy reports or complex material, similar to how children struggle with longer texts in their studies.
- Reading Fluency: Achieving a smooth and quick reading pace is another obstacle. Adults and children with ADHD might read slower and with less fluency, which can hinder their overall understanding and retention of the material.
- Varied Research Findings: Studies have shown mixed results regarding the reading abilities of those with ADHD. While some indicate notable difficulties in comprehension, others suggest that while individuals with ADHD (including adolescents and adults) may achieve average scores in certain reading tasks, their performance typically falls below that of their peers without ADHD.[12]

Impact of ADHD on Reading and Learning
ADHD, or Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, can make reading and learning tough in several ways:
- Focusing Issues: People with ADHD often find it hard to focus. This means reading and learning can be really challenging for them. They might struggle to concentrate on the text or what they're studying.
- Memory Problems: ADHD can affect someone's working memory. This is the ability to hold onto information while using it. If you can't remember what you've just read, it's hard to learn from it.
- Trouble Processing Information: Understanding or processing information can be tough for those with ADHD. This can lead to problems with understanding what they read or learn.
- Getting Distracted: People with ADHD can get easily distracted. This could be by their own thoughts or things happening around them. These distractions make it hard to stay focused on reading or learning.
- Difficulty Sitting Still: The hyperactivity part of ADHD means some people find it hard to sit still. But sitting still is often needed for reading and learning, especially in a classroom setting.
- Time Management Issues: Managing time is another challenge. This affects how well and how much they can learn within a set time.
These factors can lead to slow reading speeds and not understanding much of what they read. Also, ADHD often comes with other learning disabilities, making these problems even bigger. But with the right help and changes in how they're taught, people with ADHD can do well in learning.
It's key to talk to teachers and get extra help if needed. Getting help early and making changes in the classroom can really improve how well kids with ADHD do in school.[13][14]

Benefits Of Bionic Reading For ADHD Individuals
Bionic Reading is a special reading method that helps people, especially those with ADHD, read better. Here's how it works:
- Guiding Attention with Visual Cues: Texts can be long and tiring for people with ADHD. Bionic Reading helps by highlighting important parts. This makes it easier to focus on key information.
- Encouraging Active Engagement: The highlighted parts act like markers. They guide readers, making them more involved and helping them understand the text better.
- Aiding Retention: For those with ADHD, it's easy to forget what they've read. Bionic Reading uses visual cues to emphasize main ideas, helping remember them.
- Reducing the Strain of Re-reading: Instead of reading everything again, readers can just look at the highlighted parts. This makes reading less tiring.[15]
However, it's worth noting that Bionic Reading might not work the same for everyone with ADHD. Each person is different, so some might find the visual cues distracting. It's important to adjust the method to fit personal needs. Bionic Reading should be used along with other reading strategies, not as a replacement.[16]
Additionally, Bionic Reading isn't just for people with ADHD. It combines different reading techniques like skimming, scanning, and deep reading. This helps anyone read faster and understand better.
The main benefits of Bionic Reading include:
- Better Comprehension: By using different reading techniques, it helps understand and remember text better.
- Time-Saving: In our busy world, this method allows for quick reading, which is great for students and professionals.
- Increased Productivity: By reading efficiently, people have more time for other tasks, leading to more productivity.[17]

Implementing Bionic Reading in Daily Life
Practical tips on incorporating Bionic Reading
Incorporating Bionic Reading into your daily routines can be really helpful, especially if you're looking to improve how well you understand what you read and how fast you can read. Here are some simple tips on how to do it:
- Start Simple: Begin with easy texts. Once you're comfortable with those, move on to more complex stuff. This will help you get used to reading with Bionic Reading.
- Practice Makes Perfect: To get better at anything, you need to do it often. Try to use Bionic Reading every day. It could be for a few minutes at first, then gradually increase the time.
- Focus on Understanding: The main point of Bionic Reading is to help you understand better, not just read faster. So, take your time with each text. Make sure you really get what it's saying.
- Find a Good Spot: Choose a place where you won't be disturbed. It should be quiet and have good light. This will help you focus better.
- Be Patient: It's normal to take a while to get used to Bionic Reading. If it feels slow at first, don't worry. You'll get better with time.
- Try It on Different Things: Use Bionic Reading when you're reading anything – like a newspaper, a book, or even online articles. This will help you adapt to using it with all sorts of different texts.
Remember, the goal is to both speed up your reading and make sure you're understanding everything you read. So, give these tips a try and see how it goes!
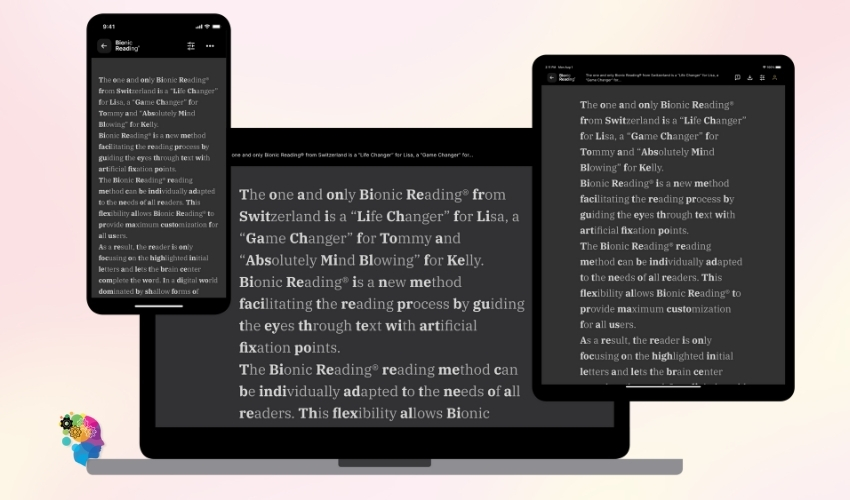
Apps And Tools For Bionic Reading
- Bionic Reading App: This is a free app you can download on your devices. It also comes with a free web browser extension. It supports various file formats, like documents and EPUB.
- Bionify: Another tool that helps with Bionic Reading.
- Jiffy Reader: This is also designed for Bionic Reading.
- BioRead: Supports Bionic Reading as well.
- Spreeder: A speed reading app that includes support for Bionic Reading.
- ReadMe: Another speed reading app that works with Bionic Reading.
- QuickReader: This app also supports Bionic Reading and is focused on speed reading.
- BionicScript: This is a free alternative you can try if you're looking for something like Bionic Reading.
- Smart Reader: Another free tool that offers an experience similar to Bionic Reading.
- Astrospeed: This app is similar to Bionic Reading, focusing on improving your reading speed.
- TorpedoRead: Like Astrospeed, this is another app that offers a reading experience similar to Bionic Reading.
Conclusion
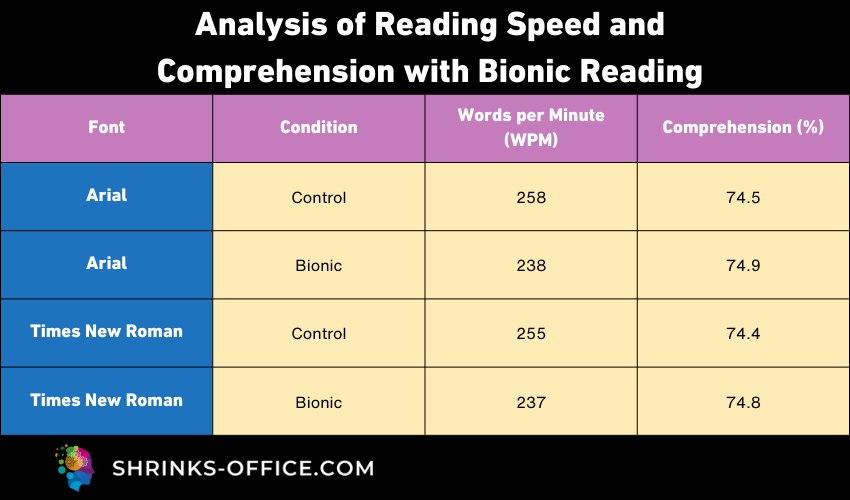
Bionic Reading represents a significant breakthrough for individuals with ADHD, offering a new horizon in reading and focus. By transforming text into a more digestible format, it creates an engaging and efficient reading experience. The comparative data on reading speed and comprehension illustrates its effectiveness, making it not just a tool for those with ADHD, but for anyone seeking to enhance their reading abilities.
This method is more than just a reading aid; it's a gateway to unlocking potential and empowering individuals to overcome challenges with attention and focus.
FAQ
What exactly is Bionic Reading and how does it help people with ADHD?
Bionic Reading is a reading method that enhances focus by highlighting the initial part of words, guiding the reader's eye and simplifying text comprehension. This technique is particularly beneficial for individuals with ADHD as it reduces the cognitive load, making it easier to maintain focus and understand the material. By providing a structured way to process text, Bionic Reading can help mitigate common reading challenges associated with ADHD.
Is Bionic Reading compatible with all types of digital devices?
Yes, Bionic Reading is versatile and can be used across a variety of platforms. It's available as an app for smartphones and tablets, both on the Apple App Store and Google Play Store, and as a browser extension for popular browsers like Google Chrome.
Can Bionic Reading replace traditional reading methods for ADHD individuals?
While Bionic Reading offers significant advantages, it is designed to complement rather than replace traditional reading methods. It acts as an additional tool that can be integrated into a person's reading strategy, especially for those with ADHD.
References
- book riot: Bionic Reading: A New Method for Reading Faster or Just Another Gimmick?
- how to geek: What Is Bionic Reading, and How Do You Use It?
- make use of: The 4 Best Bionic Reading Tools to Help You Read Faster
- basmo: What is Bionic Reading and Why You Should Care
- softlist: Unique Ways To Use the Bionic Reading Method
- Indiana Wesleyan University: What is Bionic Reading?
- Techpp: What is Bionic Reading and How to Enable it?
- Techpp: What is Bionic Reading and How to Enable it?
- Techpp: What is Bionic Reading and How to Enable it?
- readwise: Does Bionic Reading actually work?
- solopress: Bionic reading: Making readable designs
- Pubmed: Children with Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and Reading Disability
- psychcentral: How ADHD May Affect Reading
- verywellmind: The Relationship Between ADHD and Learning Disabilities
- start-teaching: Bionic Reading for ADHD
- healthline: What Are the 3 Types of ADHD?
- eagle1group: the benefits of bionic reading
- Bionic Reading App
- Bionify
- Jiffy Reader
- BioRead
- Spreeder
- ReadMe
- QuickReader
- BionicScript
- Smart Reader
- Astrospeed
- TorpedoRead





















































































































